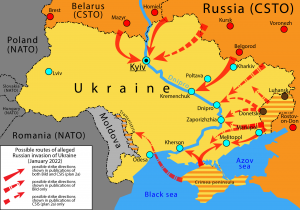
Since the commencement of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine at the end of February, different international courts and tribunals have been engaged as means to invoke international responsibility for the various violations of international law that have occurred. As is often the case in international law, however, the proceedings initiated before these tribunals reflect a very particular legal framing of the broader invasion and conduct of hostilities (I wrote on this theme a few years ago in relation to the post-2014 litigation between Ukraine and Russia). This is a consequence of the absence in international law of a single, integrated judicial system with compulsory jurisdiction. Instead, there are many different courts that, for the most part, have limited subject-matter jurisdiction. (more…)