By Dr Colin Nolden, Vice Chancellor’s Fellow researching in Sustainable City Business Models (University of Bristol Law School).*
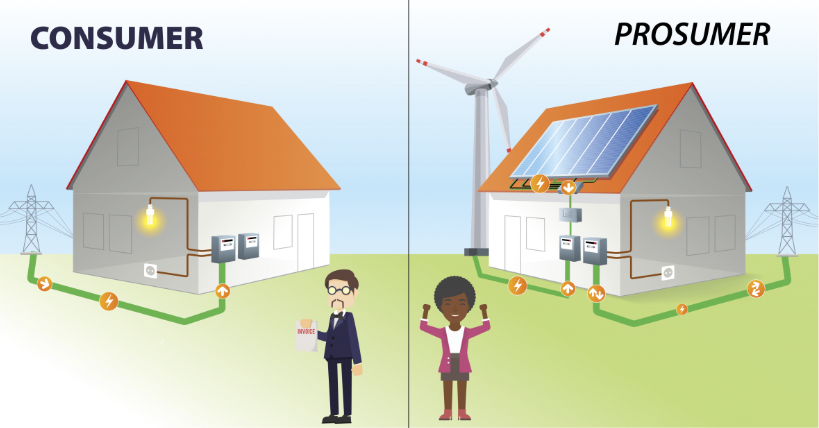
Electricity systems are undergoing rapid transformation. An increasing share of previously passive consumers is defecting energy demand and supply from the public electricity network (grid) as active ‘prosumers’ while technological and business model innovation is enabling demand-side resources to provide reliable and cost competitive alternatives to supply capacity.
Yet, centralised supply-focused market structures dominated by legacy infrastructures, technologies and supply chains associated with path-dependencies and technological lock-ins continue to dominate. Regulation has been designed around these existing supply-focused markets and structures rather than networks of the future capable of integrating and facilitating smart, flexible systems. Current systems and their regulatory frameworks are struggling to engage and integrate a range of technological, economic and social innovations promising consumer-oriented solutions to environmental problems. (more…)
