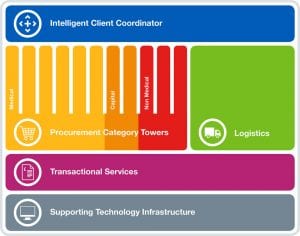
By Prof Albert Sanchez-Graells, Professor of Economic Law and Member of the Centre for Health, Law, and Society (University of Bristol Law School)
On 30 September, the Centre for Health, Law, and Society had the honour of hosting an excellent panel of speakers for a webinar on ‘Healthcare procurement and commissioning during Covid-19: reflections and (early) lessons’. The speakers provided short presentations on a host of very complementary issues surrounding the reaction of NHS procurement and commissioning to the COVID-19 challenges. The ensuing discussion brought to light a number of general themes that are, by and large, aligned with the worries that others and I had expressed at the outset of the pandemic*, and a number of challenges that will shape the readjustment or reregulation of NHS procurement and commissioning in the medium and long term.
This blogpost initially provides some brief notes on the most salient points made by the speakers in their presentations, which do not aim to be exhaustive. It then goes on to offer my own reflections and views on what lessons can be extracted from the procurement and commissioning reaction to the first wave of Covid-19, which do not necessarily represent those of the panel of speakers. (more…)